Loading...

Mastering Chicago-style citations might sound old school in the digital age, but the system is more diverse and nuanced than most realize. Many assume there is just one right way to cite, yet the Chicago Manual of Style includes two separate citation systems: Notes-Bibliography and Author-Date. This split changes the rules for nearly every type of source and reveals why even citation veterans find Chicago style both challenging and surprisingly flexible.
| Key Point | Explanation |
|---|---|
| 1. Understand Chicago style principles | Familiarize yourself with foundational aspects of the Chicago format for accurate academic writing. |
| 2. Differentiate citation methods | Choose between the Notes-Bibliography and Author-Date systems based on your discipline for proper referencing. |
| 3. Implement citations correctly | Use appropriate citation formats within your text to ensure clarity and maintain academic integrity. |
| 4. Cross-reference citations with bibliography | Ensure every in-text citation has a corresponding bibliography entry for seamless documentation. |
| 5. Verify citation accuracy meticulously | Conduct thorough checks to confirm all citations are correct and consistently formatted for scholarly credibility. |
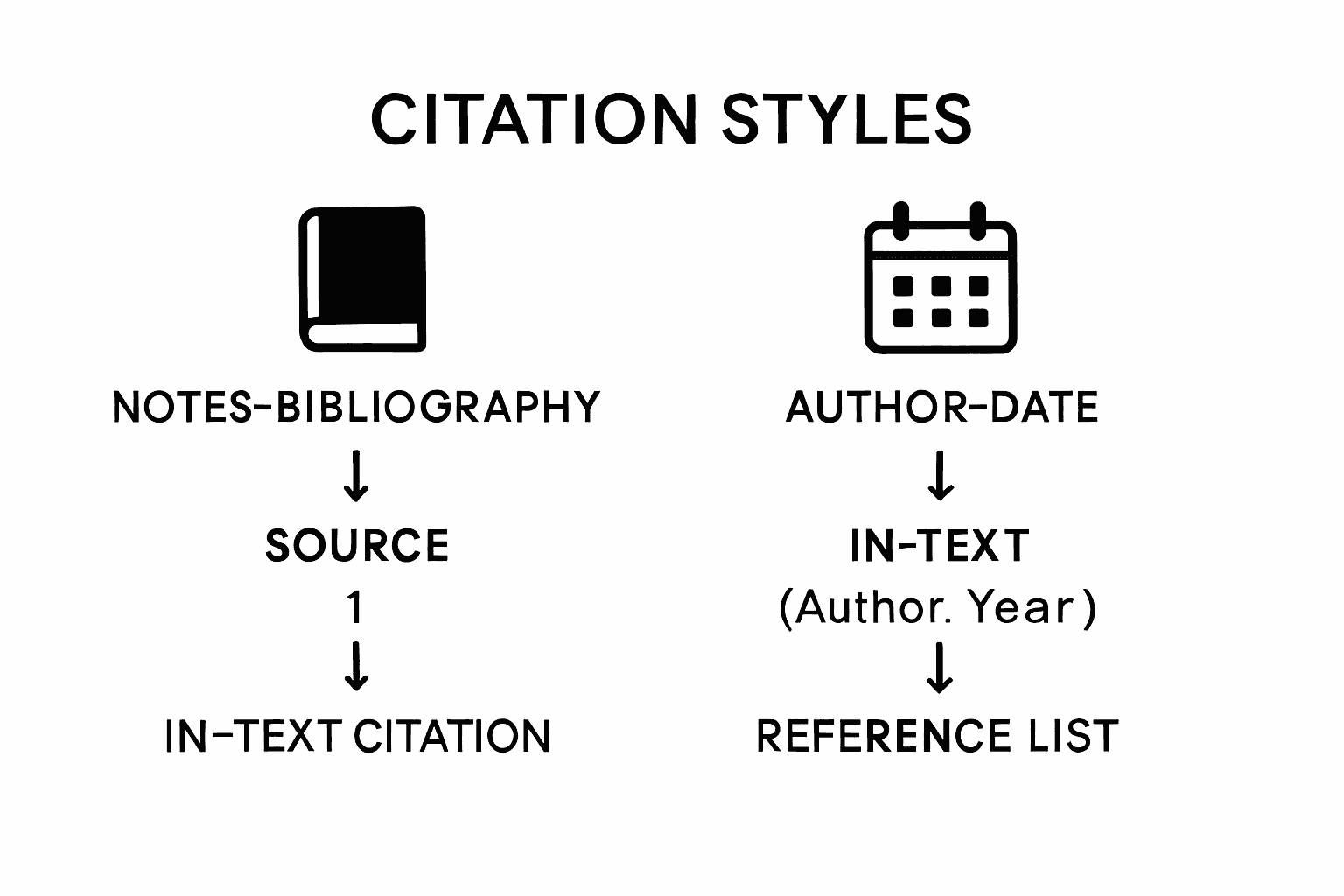
Mastering chicago format in text citation begins with understanding the foundational guidelines that govern academic writing. Navigating the Chicago Manual of Style requires a strategic approach that combines careful study and practical application. The Chicago citation system is primarily divided into two distinct methods: Notes-Bibliography and Author-Date systems, each with unique requirements for documenting sources.
Start by acquiring the most recent edition of the Chicago Manual of Style, which serves as the definitive reference for scholarly writing. Learn more about academic writing tools that can help streamline your citation process. The manual provides comprehensive details about formatting, punctuation, and source documentation that go far beyond simple citation rules.
To effectively familiarize yourself with Chicago style guidelines, focus on understanding the core principles. Pay special attention to the specific requirements of your chosen citation method for academic or research writing. The Notes-Bibliography system is typically used in humanities disciplines, while the Author-Date system is more common in sciences and social sciences. Each system has distinct rules for referencing sources within your text and creating comprehensive bibliographic entries.
Key aspects to master include:
Practical implementation is crucial. Begin by examining academic papers or journal articles in your specific field that use Chicago style. Observe how experts apply the citation guidelines in real-world writing. Create practice documents where you systematically apply the rules, comparing your work against official examples from the Chicago Manual of Style.
To help you distinguish between the two Chicago citation systems, the table below compares the Notes-Bibliography and Author-Date methods, highlighting their key features and specific usage scenarios.
| Citation System | Typical Disciplines | In-Text Method | Reference List/Bibliography Name | Main Features |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Notes-Bibliography | Humanities | Superscript numbers + notes | Bibliography | Footnotes/endnotes for in-text citation; used in history, literature |
| Author-Date | Sciences/Social Sciences | Parenthetical citation (Name, Year) | Reference List | Author and year in text; used in scientific writing |
Verify your understanding by checking your citations against official guidelines. Look for consistent formatting, correct placement of punctuation, and precise source information. A successful mastery of Chicago format in text citation means you can confidently integrate sources into your academic writing with precision and clarity.
Understanding the diverse landscape of source types is crucial for accurate Chicago format in text citation. Different sources require specific citation approaches, making it essential to recognize the nuanced rules that govern academic documentation. Explore advanced citation techniques to enhance your research writing skills.
Begin by categorizing your sources into primary groups: books, journal articles, websites, government documents, interviews, and multimedia resources. Each source type demands unique citation considerations. For books, you will need author names, publication dates, titles, and publication details. Journal articles require additional elements like volume numbers, issue numbers, and page ranges.
Web sources present unique challenges in Chicago style citation. Electronic sources need extra attention, including retrieving dates, URL information, and digital object identifiers (DOIs). Pay special attention to online publications that might lack traditional publication information. Some digital sources might require supplementary metadata to create a comprehensive citation.
Key source categories to master include:
In the Notes-Bibliography system, you will create footnotes or endnotes that provide full bibliographic information on first citation, with shortened references in subsequent mentions. The Author-Date system requires in-text parenthetical citations with a corresponding reference list. Understanding these distinctions is critical for maintaining academic integrity and providing clear source attribution.
To verify your source identification and citation skills, cross-reference your citations with official Chicago Manual of Style guidelines. Check that each source is correctly categorized and formatted according to its specific type. A successful implementation means your citations are consistent, accurate, and provide readers with comprehensive information to locate and verify your sources.
Implementing chicago format in text citation requires precision and understanding of two primary citation systems: Notes-Bibliography and Author-Date. Choosing the right approach depends on your academic discipline and specific research requirements. Discover advanced citation strategies to elevate your academic writing.
In the Notes-Bibliography system, which is predominant in humanities, you will insert superscript numbers within your text that correspond to detailed footnotes or endnotes. These notes provide full bibliographic information on first reference, with shortened citations in subsequent mentions. Placement is critical: the citation number typically follows the punctuation mark, ensuring smooth reading flow while maintaining proper documentation.
For the Author-Date system, commonly used in sciences and social sciences, in-text citations include the author's last name and publication year. Direct quotations require additional page number information. Parenthetical citations can be integrated into sentences or placed at the end of a clause. For instance, you might write "Smith (2022) argues that" or "Recent research suggests significant findings (Johnson 2022, 45)".
Key citation placement strategies include:
Pay special attention to complex scenarios like multiple authors, secondary sources, and works without clear authorship. Consistency is paramount in academic writing. Each citation should provide enough information for readers to locate the original source in your bibliography or reference list.
To verify your citation implementation, review your document for several critical elements. Check that every borrowed idea or direct quote has a corresponding citation. Confirm that your citations follow the chosen Chicago style system uniformly. A successful implementation means your citations are clear, precise, and provide transparent attribution to original sources.
Cross-referencing your in-text citations with the bibliography is a critical step in maintaining academic integrity and ensuring precise source documentation. The goal is to create a seamless connection between your text citations and the complete reference list. Explore advanced research documentation strategies to refine your academic writing skills.
Begin by creating a comprehensive bibliography that follows the specific requirements of your chosen Chicago style system. In the Notes-Bibliography method, your bibliography will appear as a separate page at the end of your document, listing all sources referenced in full bibliographic format. For the Author-Date system, you will create a reference list that provides complete publication details for each source mentioned in your in-text citations.
Systematic verification is crucial to ensure every in-text citation has a corresponding full reference. Develop a methodical approach by creating a cross-reference checklist. Start by reviewing each in-text citation and confirming it appears exactly in your bibliography or reference list. Pay close attention to details like author names, publication years, page numbers, and source titles.
Key cross-referencing strategies include:
Address potential challenges by carefully managing complex sources such as multiple authors, translated works, or digital publications. Attention to detail separates good academic writing from exceptional scholarly work. For each source, confirm that the in-text citation provides enough information to direct readers precisely to the full reference in your bibliography.
To verify your cross-referencing, conduct a systematic review. Print out your document and physically check each citation against its corresponding bibliography entry. Alternatively, use digital tools that can help track and match citations. A successful cross-reference means every source mentioned in your text can be easily located in your bibliography, with consistent and accurate information that meets Chicago style guidelines.

The final stage of mastering chicago format in text citation involves a meticulous review process that ensures the absolute accuracy of your source documentation. Verification is more than a simple proofread - it is a comprehensive examination of your academic writing's structural and methodological integrity. Discover advanced citation verification techniques to elevate your scholarly work.
Begin your review by systematically comparing each in-text citation against its corresponding bibliography entry. Precision is paramount: examine every detail including author names, publication years, page numbers, and formatting consistency. Use digital tools or manual checklists to track your verification process, ensuring no citation goes unchecked.
Pay special attention to complex citation scenarios that frequently trigger errors. Multimedia sources, translated works, and digital publications require extra scrutiny. Check that your citations follow the specific guidelines of your chosen Chicago style system - whether Notes-Bibliography or Author-Date. Inconsistent formatting can undermine the credibility of your entire research document.
Key verification strategies include:
Technological tools can significantly streamline your verification process. Citation management software and academic writing platforms offer automated checking mechanisms that can identify potential citation discrepancies. However, remember that these tools are assistants, not replacements for careful human review.
To confirm successful citation verification, establish a comprehensive checklist. Confirm that each source is accurately represented, formatting is uniform, and no citation errors remain. A successful review means your document meets the highest academic standards - transparent, precise, and meticulously documented. Your final document should reflect not just the content of your research, but your commitment to scholarly excellence.
Use the checklist below during your final review to ensure every Chicago in-text citation and bibliography entry meets required academic standards before submission.
| Verification Step | Description | Complete (Yes/No) |
|---|---|---|
| Match every in-text citation to bibliography | Ensure all citations are cross-referenced | |
| Check formatting consistency | Confirm uniform citation style throughout | |
| Verify author names and publication years | Ensure accurate and complete details for each source | |
| Review page numbers and publication information | Check for correct page ranges and edition details | |
| Inspect punctuation and capitalization | Adhere to Chicago style rules for each entry | |
| Double-check complex/online sources | Pay extra attention to digital and multimedia citations | |
| Utilize digital tools or checklists | Employ citation management platforms for extra assurance |
Tired of spending hours double-checking every note and reference to meet strict Chicago style requirements? When mastering complex citation rules like in-text citation markers, footnotes, and bibliographic cross-referencing, even the most diligent writers feel overwhelmed. Making one small mistake can undermine your credibility and create unnecessary stress with every draft. If you are seeking clarity and peace of mind, Samwell.ai was designed with your academic integrity at heart.

Imagine having an advanced AI platform that checks every Chicago Manual detail for you, so you can focus on your ideas and analysis instead of formatting stress. Samwell.ai uses intelligent technology to verify your sources, align your work with the latest citation guidelines, and help you avoid easy-to-miss mistakes. Whether you need help with in-text citations or want your bibliography perfectly cross-referenced, the Samwell.ai suite includes tools like the 'Power Editor' for targeted citation improvements and real-time verification features to uphold scholarly excellence. Start using Samwell.ai today and turn citation mastery into an automatic part of your writing process.
The two main Chicago citation systems are the Notes-Bibliography system and the Author-Date system. The Notes-Bibliography system is primarily used in humanities disciplines, while the Author-Date system is more common in sciences and social sciences.
In the Notes-Bibliography system, use superscript numbers within your text, which correspond to footnotes or endnotes. In the Author-Date system, include the author's last name and publication year in parentheses, with page numbers for direct quotes.
Your bibliography should include full bibliographic details for each source referenced in your work. Elements typically included are author names, publication dates, titles, and specific publication details relevant to the type of source being cited.
Verify your citations by cross-referencing each in-text citation with its corresponding bibliographic entry. Ensure all details match, including author names, publication years, and formatting. Utilizing digital tools or checklists can help streamline this verification process.



